Custom Thermoformer Relies On Robotic Trimming
Processor Strategies: Ray Products
Fully robotic, six-axis trimming has improved speed and quality while cutting costs for this former.
A lot has changed since thermoformer Ray Products was founded in 1949 by Allen Ray. For Brian Ray, company president and part of the third generation of family ownership, one of the most important changes is in his plant’s trimming operations.
Operating from an ISO 9001:2008 certified, 48,000 ft² plant in Ontario, Calif., Ray Products offers what it says is the largest thermoforming part-size capacity on the West Coast—up to 10 x 18 ft with draws up to 40 in. deep—along with dedicated in-house painting and finishing capabilities. In the old days, the company made primarily one product: baby bassinets. Today, Ray Products makes custom parts that are used globally in everything from medical devices to commercial aircraft. Its large-part capabilities allow it to form single parts that previously had to be made out of either fiberglass composite or an assembly of multiple parts.
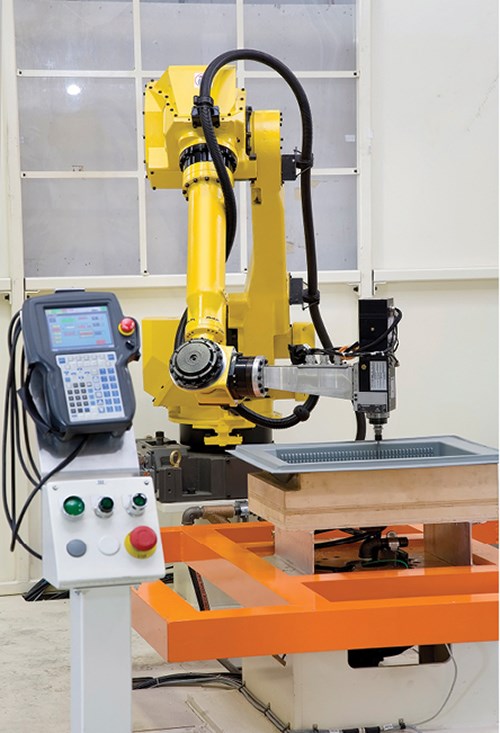
A lot of this can be attributed to the company’s commitment to fully robotic trimming. “For many years, all trimming by us was done by hand,” Brian Ray recalls. “Some companies in our business still trim by using air-powered, handheld routers. We’ve chosen to implement fully robotic, six-axis routing stations. Every project we produce is trimmed by one of our robots.”
“Made by hand” may be nice if you’re buying a watch, but in Brian Ray’s viewpoint there is no going back in time on robotic trimming. He cites three reasons to justify his commitment to this technology:
•Speed—Ray Products’ robotic trimmers run at over 500 in./min. “Even the most talented human trimmers working under ideal conditions could never cut that much plastic in a minute, particularly not with any kind of accuracy,” Ray points out. “If we were to pull out our robotic trimming stations and go back to handheld trimming, there’s no question trimming would immediately become the bottleneck in our factory. That would mean both increased costs and longer turnaround times for our customers.”
•Quality—“It’s no accident that when we’re describing something that’s very accurate, we use the term ‘robotic precision,’” says Ray. “Robots get it right every time. They don’t drink too much coffee and get shaky hands. They don’t sneeze mid-cut. They don’t get full and tired after a big lunch.”
Ray says the robotic trimmers can be accurate to within ±0.004 in. Industry-standard thermoforming tolerances start at ±0.010 in., so robotic trimming is a critical step in helping the company reach its goal of “consistently exceeding the industry standard,” he says.
“Quality is something we focus on,” he states. “Earlier this year we conducted a survey. We asked companies to rank the things they look for when they’re picking a thermoformer. Quality was their number-one choice. And robotic trimming is key to us achieving high levels of quality.”
•Cost—It may seem counterintuitive to list cost as a benefit of robotic trimming. After all, robotic trimming requires robots, which are big, complex machines with lots of moving parts that don’t come cheap. Says Ray, “Yes, robotic trimming requires a significant initial investment. However, the cost benefits that come from this investment are too big to ignore. It’s hard to overstate the cost benefits of getting it right the first time. Robotic trimming reduces mistakes and their associated cost, and lets us deploy our skilled workforce in more productive ways. When it comes down to it, fully robotic trimming lets us offer our customers more competitive pricing and a higher quality product, in less time.”
Nearly 65 years ago, when Allen Ray founded the company, he delivered high-quality thermoformed products without robotic trimming. “Today, I don’t think we could be a competitive manufacturer without robotic trimming stations,” his grandson states.
Related Content
Sustainable Materials is Focus of Thermoforming Exhibits at K 2022
Thermoforming equipment makers including WM, Kiefel, and OMV will showcase processing of recyclable and biobased materials.
Read MoreAutomation in Thermoforming on the Rise
Equipment suppliers’ latest innovations exemplify this trend driven by factors such as labor shortages, higher-speed thermoformers and tighter quality control.
Read MoreEnhanced Digitization in Thermoforming
Illig’s Easy product family includes the newly developed Human Machine Interface, Illig Easy Touch.
Read MoreIngenuity Is Part of This Former’s Name, and in Its DNA
Plastic Ingenuity started in a garage in 1972 and through a commitment to developing best-in-class products stands today as one of the largest custom thermoformers in the world.
Read MoreRead Next
Medical Device Nabs Thermoforming Award
A thermoformed medical device from Ray Products won first place in the Heavy-Gauge, Pressure-Formed category at the SPE Thermoforming Div. annual parts competition, held recently in Atlanta.
Read MorePeople 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
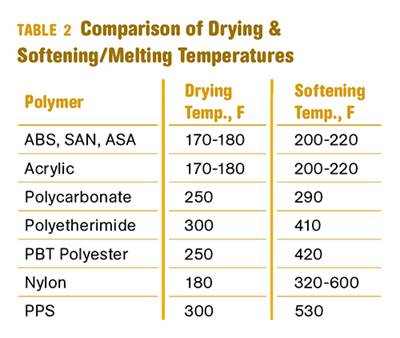
Read MoreWhy (and What) You Need to Dry
Other than polyolefins, almost every other polymer exhibits some level of polarity and therefore can absorb a certain amount of moisture from the atmosphere. Here’s a look at some of these materials, and what needs to be done to dry them.
Read More



















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)