PE Film Market Analysis: Geomembrane Liners
Market to average 3.4% growth over the next two years.

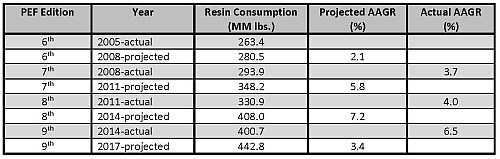
In 2014, approximately 400.7 million lb of PE resins were consumed in the production of geomembrane lining systems. With an average annual growth rate of 3.4%, total PE resin consumption for this market is expected to reach 442.8 million lb by 2017.
These are among the conclusions of the most recent study of the PE Film market conducted by Mastio & Co., St. Joseph, Mo.
According to Mastio, geomembrane liners are typically divided into four major groups :
Waste containment: Waste containment applications include hazardous, industrial, and municipal waste. Hazardous landfills, landfill caps, chemical ponds, wastewater lagoons, and solid waste landfills are the most common applications for waste containment geomembrane lining systems. Toxic pollutants in household garbage come from chemicals in cleaning products, paints, oils, insecticides, solvents and other products. The PE liner layer protects surrounding soil and groundwater from toxic chemicals.
Liquid containment: Liquid containment applications include lining systems for aquaculture markets, such as potable water, recreational containment, water conveyance, earth dams, and lining tanks and ponds. The liquid containment market is growing steadily due to international reconstruction of water reservoirs requiring lining systems and floating covers.
Mining applications: Mining, also known as heap leach mining, utilizes synthetic liners to contain chemicals used in extracting minerals such as gold, silver, and copper from ores. The leaching process requires a liner to contain the ore which has been sprayed with cyanide or other chemicals to extract the minerals. The chemical extract is then drained into a holding pond where the minerals are removed from the solution by an electrolytic process. Blast hole liners are used for lining blast holes in the mining industry. As the liner is lowered into a blast hole, the pointed shape of the lower end tends to center the liner in the hole. Upon reaching the bottom of the hole the weighted pocket sags to one side of the hole and allows later added explosive material to be received at the very bottom of the hole.
Specialty/other applications: These consist of decorative pond liners, tunnels and irrigation canals, cutoff walls, dams, vapor barriers, highway construction, and additional temporary and lightweight lining applications.
Geomembrane lining systems typically have a minimum thickness of 20 mils and a maximum of 120 mils, Mastio says. However, custom liners can range in thickness from 4 mils to 300 mils. The most common gauge for geomembrane liners is 60. Due to the thickness of this product, geomembrane liners are typically referred to as sheet rather than film.
Most geomembrane liners must be over 20-mils thick to insure longevity. Only a small portion of geomembrane liners are less than 20 mils and are recommended for specialty applications, such as water barriers for potable water and non-potable water.
Geomembrane liner dimensions vary according to the application and the gauge, states Mastio. Geomembrane liner widths range from 15 ft to 34.5 ft with a typical width of 22 to 23 ft. Liner length varies according to the gauge and weight of the liner. The dimensions of a typical 60-mil geomembrane liner are 23-ft-wide by 500-ft-long totaling an area of 11,500 ft².
Geomembrane liners are extruded and shipped in rolls, Mastio notes. Roll weights vary from 2500 lb up to 7500 lb depending upon liner dimensions and thickness. The roll weight for a typical 60-mil, 23-ft-wide by 500-ft long liner is approximately 3400 to 3900 lb, with a core weight ranging from 40 to 70 lb. Geomembrane liner rolls are shipped on flatbed trailer trucks. Rolls that are shipped overseas are transported in open or closed top containers. Typically, up to 12 full rolls can be shipped per truckload or container.
Geomembrane liners are specifically designed for prolonged exposure to elements in which they are intended. HDPE resin is the most common PE material used in the production of geomembrane liners.
MATERIAL ALTERNATIVES
According to the Mastio research, geomembrane liners are typically made from materials such as HDPE, LLDPE, PVC, chlorosulfinated PE, chlorinated PE , and PP, which are designed primarily for containment, water treatment, and protection. Several critical properties, such as flexibility, high strength, durability, puncture resistance, UV stability, and chemical resistance are expected of a high quality lining system.
TECHNOLOGY TRENDS
During 2014, the most common process utilized in the production of geomembrane liners was blown film extrusion, accounting for 72.7% of PE resin consumption. Sheet extrusion accounted for the rest,
Blown film extrusion requires very large dies to manufacture geomembrane liners, normally 86 in. dia. A roll width of 22.5-ft can be produced with a 1:1 blow-up ratio. Widths up to 48 ft. can be achieved by increasing the blow-up ratio, but the increased widths decrease the number of rolls that can be placed on a flatbed truck, increasing transportation costs.
Both monolayer and coextruded structures are produced for geomembrane liners. In 2014, multi-layer coextruded PE film accounted for 52% of the market. Usually these are two- or three-layer structures.
Related Content
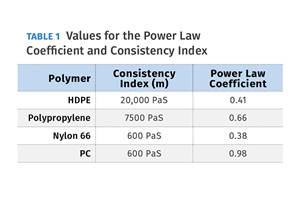
The Importance of Viscosity in Melting
The calculations required to determine the right melt temperature for each polymer are complicated. Knowing the power-law coefficient and the consistency index of the polymer you run might prove useful.
Read MoreHow to Estimate and Control Head Pressure
You rightfully worry about melt temperature, but don’t overlook head pressure, because the two are closely linked and will influence line performance.
Read MoreAvoid Four Common Traps In Granulation
Today, more than ever, granulation is an important step in the total production process. Our expert explains a few of the many common traps to avoid when thinking about granulators
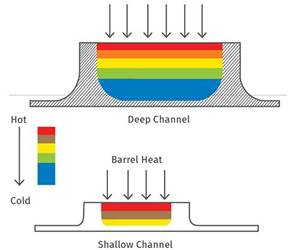
Read MoreThe Importance of Barrel Heat and Melt Temperature
Barrel temperature may impact melting in the case of very small extruders running very slowly. Otherwise, melting is mainly the result of shear heating of the polymer.
Read MoreRead Next
Advanced Recycling: Beyond Pyrolysis
Consumer-product brand owners increasingly see advanced chemical recycling as a necessary complement to mechanical recycling if they are to meet ambitious goals for a circular economy in the next decade. Dozens of technology providers are developing new technologies to overcome the limitations of existing pyrolysis methods and to commercialize various alternative approaches to chemical recycling of plastics.
Read MorePeople 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
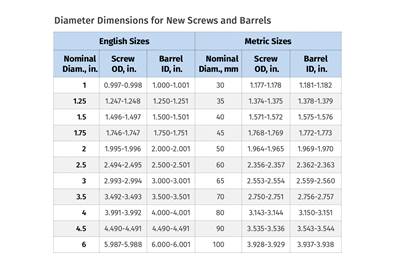
Read MoreTroubleshooting Screw and Barrel Wear in Extrusion
Extruder screws and barrels will wear over time. If you are seeing a reduction in specific rate and higher discharge temperatures, wear is the likely culprit.
Read More