Diesel Fuel Made from Recycled Plastic Undergoing Trials
Plaxx is the product of polymerizing mixed plastic waste into a substance consisting of hydrocarbon monomers similar to crude oil.
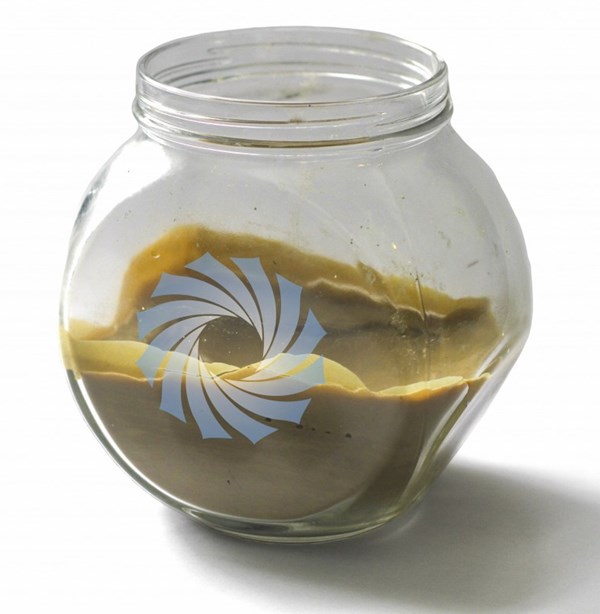

Plaxx is the product of polymerizing mixed plastic waste into a substance consisting of hydrocarbon monomers similar to crude oil.
New research will determine if Plaxx, made from residual mixed plastic waste, can be used efficiently in diesel engines which currently use HFO (Heavy Fuel Oil), without increasing engine wear. These engines are in marine vessels such as tankers, ferries, as well as other nautical machinery.
The research, funded by Innovate UK and ESPRC will be led by Associate Professor Farid Dailami, Bristol Robotics Laboratory (BRL), in partnership with Recycling Technologies, developers of Plaxx. The project is also supported by Swindon Borough Council, Crapper and Sons Landfill Ltd., and an international marine insurer.
In addition to the shipping industry, the research is also of interest to waste treatment companies, packaging manufacturers and local waste handling authorities. According to the researchers, its long term application helps create a useable resource from waste that isn’t efficiently recycled mechanically.
The waste source is the plastic entering the commercial, industrial and municipal waste streams that is mixed, laminated, contaminated and otherwise not processable by conventional plastics recycling techniques. Plaxx is the product of the polymerization of plastic and is made up of a mixture of hydrocarbon monomers similar to crude oil. It is reportedly very low in sulphur and other organic and inorganic contaminants. Currently it is a soft wax at room temperature but a low viscosity liquid at 70°C. The researchers say that it can be further refined and could be used as an input to plastics manufacturing.
The research will develop the use of Plaxx by testing engine performance, exhaust emissions and engine wear on different engines over a broad range of test conditions. The research will also develop software tools that will monitor these three aspects to enable engine users to achieve optimum performance from Plaxx.
“This new fuel could have huge environmental benefits as an alternative to HFO currently used in marine diesel engines and industrial engines,” says Associate Professor Farid Dailami. “Our research will compare the performance of this fuel with standard diesel fuel in order to gain data on how it performs and to ensure it won't damage the engine or cause harmful emissions or gases. The aim is to demonstrate to producers and users of these engines that Plaxx can be a viable alternative to HFO and to pave the way for commercialization of Plaxx.”

Related Content
-
Evolving Opportunities for Ambitious Plastics Recycler
St. Joseph Plastics grew from a simple grinding operation and now pursues growing markets in recycled PP, food-grade recycled materials, and customized post-industrial and post-consumer compounds.
-
Avoid Four Common Traps In Granulation
Today, more than ever, granulation is an important step in the total production process. Our expert explains a few of the many common traps to avoid when thinking about granulators
-
A Recycling Plant, Renewed
Reinvention is essential at Capital Polymers, a toll recycler that has completely transformed its operation in a short period of time.