The 5 M’s of Molding—Part 3: Material
You’ve accounted for variability in two other “Ms”—mold and man—but materials in their lot-to-lot differences and handling challenges pose a distinct threat to repeatability.
You’ve accounted for variability in two other “Ms”—mold and man—but materials in their lot-to-lot differences and handling challenges pose a distinct threat to repeatability.
Material: One of the fundamental considerations in processing is the material being used. Processing relies heavily upon the consistency and quality of the plastic that has been chosen for the part’s aesthetic and dimensional make up. Here are some of the primary variables that need to be reviewed during the stages of process development and in some cases continuous improvement.
Properties: Every material has its own unique set of molding properties that must be considered as a molding operation is developed. Here is a list of some of these properties as they relate to part aesthetics and dimensions:
Temperature- Mold and barrel temperatures are a huge part of the molding equation. Some examples of potential heat-related deficiencies would be long cycles, warping, burn at end of fill, gassing, etc.
Shrinkage- Every material has its own rate of shrinkage and this is one key measurable that should be considered as material choice is being decided.
Melt Flow: Material viscosity is a key component during process development and improvement review. For instance, a heavily ribbed part might be better suited with a material with a low viscosity to assure that the flowfront moves quickly across the ribs preventing an overpack condition.
Aesthetics & Dimension: There are many variations on engineered materials that either benefit or detract from the overall performance and functionality of part production. Utilize the knowledge and resources of your material manufacturer whenever possible to find the appropriate material solutions.
Additives: There are many situations where material additives can create problems or provide solutions. For instance, the use of color mixing may seem cost effective, yet generate scrap due to poor diffusion leading to faulty parts via color swirls. Or from a different perspective, adding a lubricant to polypropylene might eliminate parts sticking in a mold where draft cannot be added. Work with your material supplier to develop and/or improve a part’s molding capabilities.
Drying: Drying is always a major factor in process consistency. Verify that your dryer throughput is sufficient enough to allow adequate time to properly dry the material being used. It is also important to verify that the material is truly dry through moisture analysis.
Characteristics: When choosing a material, it is important to understand what the typical characteristics are regarding a material’s performance and drawbacks. For instance, nylon has a tendency to shrink; polypropylene tends to have sink issues over large or deep ribs. Look for materials that match the functionality of the part being molded while avoiding potential problems associated with material choice.
Garrett MacKenzie is the owner and editor of www.plastic411.com. Mackenzie started in plastics at the age of 19 as an operator, eventually moving up through the ranks to engineering and management over a 29-year timeframe. He currently works as a plastic injection consultant in engineering and training capacities. He can be contacted at garrett.mackenzie@mail.com.
Next week, Part 4 in The Five “Ms” of Molding: The Machine

Related Content
Injection Compression Molding as Alternative to Thermoforming
Arburg will show its all-electric Allrounder 720 A press utilizing injection compression molding to create thin-wall IML cups from PP.
Read MoreCompact Hybrid Injection Molding Machine Launched
Sumitomo Heavy Industries Ltd. (SHI) has introduced the iM18E, promising the smallest footprint in 20-ton machines.
Read MoreIPEX Opens Injection Molding Facility in North Carolina
The pipe and fittings manufacturer’s new 200,000-square-foot facility represents a $200 million investment and will create 150 jobs.
Read MoreAbsolute Haitian Brings Next Generation of Presses to Orlando
Absolute Haitian says Generation 5 of the servo-hydraulic Haitian and electric Zhafir machines lines emphasize efficiency, performance and intelligence.
Read MoreRead Next
Processor Turns to AI to Help Keep Machines Humming
At captive processor McConkey, a new generation of artificial intelligence models, highlighted by ChatGPT, is helping it wade through the shortage of skilled labor and keep its production lines churning out good parts.
Read MorePeople 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
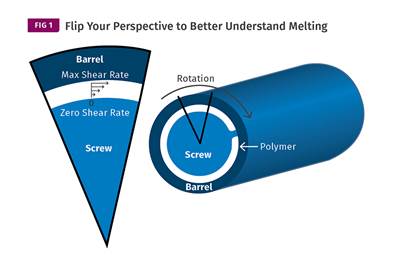
Read MoreUnderstanding Melting in Single-Screw Extruders
You can better visualize the melting process by “flipping” the observation point so that the barrel appears to be turning clockwise around a stationary screw.
Read More