New Ethylene Acrylate Copolymers Try Out for Impact-Modifier Roles
Cost-effective toughening of both commodity and engineering thermoplastics is one of the roles envisioned for a line of specialty ethylene copolymers newly available from DuPont Packaging and Industrial Polymers, Wilmington, Del.
Cost-effective toughening of both commodity and engineering thermoplastics is one of the roles envisioned for a line of specialty ethylene copolymers newly available from DuPont Packaging and Industrial Polymers, Wilmington, Del. The Elvaloy AC resin family includes eight ethylene methyl acrylates (EMAs), four ethylene ethyl acrylates (EEAs) and six ethylene butyl acrylates (EBAs). They range in melt flow from 0.4 to 9.0 g/10 min, and acrylate content runs from 7% to 27%.
Besides impact modification, the new resins can be used on their own in molding and extrusion for packaging and durable applications. They also have potential as masterbatch vehicles. They boast much greater thermal stability than EVAs, whose heat resistance is marginal in some applications. What’s more, Elvaloy AC resins reportedly have higher melting points and melt strength than similar acrylate copolymers on the market.
This family is the product of DuPont’s year-old manufacturing joint venture with Borealis AS of Denmark. The joint venture, called Speciality Polymers Antwerp (SPA) is based in Antwerp, Belgium. SPA operates a tubular reactor with capacity of 275 million lb/yr.
Global marketing of the copolymers is being handled mainly by DuPont. Says Bernard Rioux, global marketing manager for the new resin family, “These new ethylene acrylate copolymers give us a number of new performance features that are relatively undeveloped in the markets we serve.”
Structural differences
Most of today’s ethylene copolymers are made in high-pressure autoclaves equipped with powerful mixers in the polymerization chamber to achieve homogeneous output. In contrast, SPA’s tubular reactor technology relies on passage through a very long polymerization chamber, rather than strong mixing, to complete the copolymerization. The resulting copolymers are somewhat heterogeneous materials with different branching and molecular-weight distribution. They offer the physical and mechanical characteristics of more homogeneous copolymers made with similar comonomer levels. However, the more heterogeneous materials behave unlike autoclave copolymers in certain important aspects, according to Barbara Glazar, DuPont’s marketing manager for the new resins in North America.
For example, at a given comonomer or flexibility level, Elvaloy AC copolymers have higher viscosity and melt strength than other resins on the market. This is helpful in extrusion or blow molding applications, whether Elvaloy AC acts as a modifier or the matrix resin.
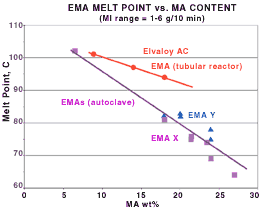
Secondly, melting points of conventional ethylene acrylate copolymers drop as acrylate levels increase. This creates a trade-off in applications where high acrylate levels are desired for greater toughness or flexibility, but where high melt point is needed. Elvaloy AC resins have higher melting points than competing copolymers of similar acrylate content, says Glazar (see Fig. 1). As a result, Elvaloy AC is finding applications in polymer modification where its higher melting point helps prevent stickiness or bridging in the feed zone or where end-use temperatures of the final product will be higher.
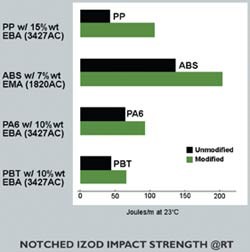
Performance of these highly polar acrylate copolymers as tougheners appears particularly interesting in thermoplastics such as PP and TP polyester. As shown in Fig. 2, adding 15% of an EBA with 27% acrylate level to PP boosts notched Izod impact by two to three times at room temperature. Low-temperature toughening properties of these acrylates also appear attractive, according to Glazar.
DuPont has examined a number of polymer systems, including PP, PBT, ABS, PBT/ABS, PC, and nylon, for compatibility with the new tougheners. A number of resin manufacturers are studying different acrylates and additive levels to optimize performance. “We’re finding interest in these materials as general-purpose tougheners,” says Glazar. “These acrylates are proving versatile across a wide range of resins in achieving notched Izod values up to two times that of the unmodified base resin.”
Thermally stable
Besides impact modification, masterbatch uses are proving among the most interesting of the new application areas for the new acrylates. Because of their heat stability, Elvaloy AC resins can be used as masterbatch resins for coloring engineering thermoplastics that have typically been out of range for conventional EVAs. Resistance to degradation can be raised by 40 to 80° C (100 to 175° F) by using copolymers other than EVA.
“Working with the new copolymers, compounders and processors can formulate wider-serving masterbatches and, in some cases, eliminate the number of pigmenting systems required for their customers,” says Glazar. She reports interest from producers of PA, PBT, PC, ABS, PP and PE masterbatches.
Latest developments
DuPont will shortly announce the availability of a new FDA-compliant, food-grade, high-comonomer EMA resin, Elvaloy 1224 AC (24% acrylate). It has potential both as a modifier and on its own. Says Glazar, “There’s an upper limit on comonomer level for FDA food contact. One of our first targets for expanding the AC line-up has been the upper end of what will meet FDA guidelines. People want all the property improvements they can get from the higher MA level, while staying FDA compliant.”
For more details, including property data on each of the 18 Elvaloy AC grades, visit the new web site: www.dupont.com/industrial-polymers/elvaloy/acindex.html.
Related Content
Understanding the ‘Science’ of Color
And as with all sciences, there are fundamentals that must be considered to do color right. Here’s a helpful start.
Read MoreGerdau Graphene Launches “First” Graphene-Enhanced PE Additive Masterbatch for Extruded Packaging and More
The company has also partnered with conglomerate Sumitomo Corp. for distribution of its graphene-enhanced masterbatches in Japan.
Read MoreResins & Additives for Sustainability in Vehicles, Electronics, Packaging & Medical
Material suppliers have been stepping up with resins and additives for the ‘circular economy,’ ranging from mechanically or chemically recycled to biobased content.
Read MoreMasterbatches Reduce Gloss in PLA and PETG 3D Printed Products
Insight Polymers & Compounding’s two low-gloss additive masterbatches shown to boost appearance of 3D printed objects.
Read MoreRead Next
Lead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
Read MoreUnderstanding Melting in Single-Screw Extruders
You can better visualize the melting process by “flipping” the observation point so that the barrel appears to be turning clockwise around a stationary screw.
Read MorePeople 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
Read More












.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)