Novel Liquid Modifiers for Polyolefins Have Multiple Functions
A family of liquid polymer modifiers with a proven track record in EPDM compounds has been expanded for use in a broad range of polyolefins.
A family of liquid polymer modifiers with a proven track record in EPDM compounds has been expanded for use in a broad range of polyolefins. These additives are said to break the mold of conventional plasticizers in their enhancement of both physical properties and processability. Depending on the application and polyolefin system, they can act as processing aid, flow enhancer, compatibilizer, toughener, and plasticizer.
New Elevast polymer modifiers from Houston-based ExxonMobil Chemical are non-phthalate specialty hydrocarbon fluids. They range in viscosity from 25 to 2800 cps at 25 C. The first grades are fully paraffinic, though future products soon to be added will include non-paraffinic types. Elevast modifiers are designed for LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE, PP homopolymers and copolymers, TPOs, metallocene-catalyzed plastomers (ExxonMobil’s Exact and Dow Chemical’s Engage), and novel olefin elastomers like ExxonMobil’s Vistamaxx and Dow’s Versify. They also have some compatibility with styrenic TPEs such as those based on SEBS.
Among the benefits they reportedly offer are greater softness and flexibility, lower brittleness temperature, higher elongation, and improved optics. According to product manager David Dunaway, Elevast modifiers have potential in a wide range of applications: wire and cable; pipe and tubing; flexible packaging; automotive, appliance, consumer, and industrial parts; and compounding of TPO, TPV, TPE, and EPR thermoplastic elastomer blends. Several applications in these areas are already commercial.
ROLES THEY CAN PLAY
Among their many possible functions, Elevast modifiers can be used in a TPO formulation to provide an improved toughness/stiffness balance, according to Dunaway. He says the new additives are synergistic with plastomers used as impact modifiers in TPO: “They can lower the brittleness temperature and allow processors to use lower loadings of plastomer while also enhancing processability, such as long flow for large parts such as auto bumper fascias.”
In wire and cable, Elevast can be used to increase flexibility. When used in a Vistamaxx thermoplastic elastomer, it will enhance elasticity. Dunaway explains that Elevast modifiers reside in the polymer’s amorphous, not crystalline, region. As a result, melt temperature and crystallization temperature are unaffected. HDT is only slightly reduced by the dilution of the crystalline phase in the modified polymer. “An Elevast polymer modifier is miscible because it remains in the amorphous phase. That is why in wire and cable, it allows processors to use a higher-density and lower-MI resin for higher heat resistance while maintaining good flexibility and processability.”
Elevast can be blended with an LDPE, HDPE or LLDPE to provide better flexibility, durability, and processability. According to Dunaway, Elevast can help processors improve compound properties by using low-MI resins that are hard to process in highly filled formulations. In addition, Elevast can be used in flame-retardant compounds. Because of their extremely high flash point (>225 C), these modifiers can help disperse FR additives or fillers without any detrimental effect on properties and also allow for higher throughput.
HARD & SOFT TPO’S
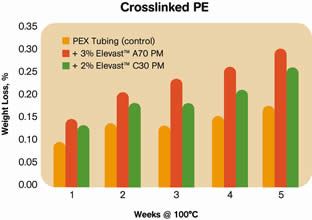
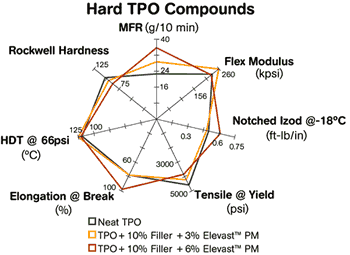
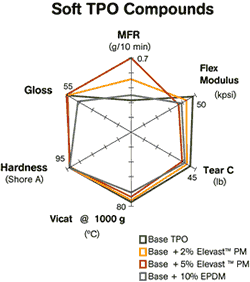
Elevast polymer modifiers have been demonstrated to offer advantages in both hard and soft TPO formulations. In hard TPOs, Elevast improves processing speeds, reduces scrap, improves surface finish, reduces weight, and allows for lower injection and clamp pressures. As previously noted, it can help TPOs achieve a new balance of stiffness, toughness, and processability and use higher filler content. Similarly, in soft TPOs, Elevast can decrease stiffness, increase elongation, and enhance processability, especially in highly filled compounds.
The idea of adding a liquid modifier to polyolefins may initially make some processors hesitant. But Dunaway says Elevast is highly compatible with most polyolefins. At typical incorporation levels of 1% to 5%, there is “near zero” exudation.
This modifier can be injected directly into the feed throat or vent ports of an extruder via a liquid metering pump such as the sort used for liquid colorant. In its compounding guide, the company recommends that Elevast be injected into the barrel at a point after the polymer has melted. If fillers also are being added, the injection point should be after the fillers have been introduced and dispersed. Injection pressure for the liquid additive should be at least 600 psi.
Related Content
Engineering Resins Compounder Expands to Take on More Scrap
Polymer Resources responds to sustainability push by upgrading plant with grinding and shredding equipment to take on both postindustrial and postconsumer reclaim.
Read MoreHow to Configure Your Twin-Screw Barrel Layout
In twin-screw compounding, most engineers recognize the benefits of being able to configure screw elements. Here’s what you need to know about sequencing barrel sections.
Read MoreHow to Maintain Pelletizing Quality When Acid Attacks
Developments in the chemistry of polymers and additives have made corrosion a real problem in pelletizers. Here’s how to ward it off.
Read MoreHow to Configure Your Twin-Screw Extruder: Part 3
The melting mechanism in a twin-screw extruder is quite different from that of a single screw. Design of the melting section affects how the material is melted, as well as melt temperature and quality.
Read MoreRead Next
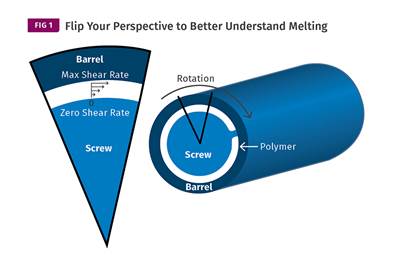
Understanding Melting in Single-Screw Extruders
You can better visualize the melting process by “flipping” the observation point so that the barrel appears to be turning clockwise around a stationary screw.
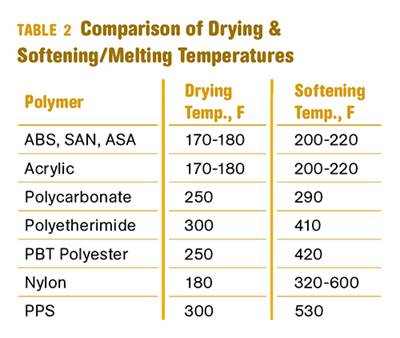
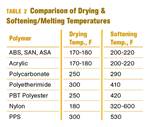
Read MoreWhy (and What) You Need to Dry
Other than polyolefins, almost every other polymer exhibits some level of polarity and therefore can absorb a certain amount of moisture from the atmosphere. Here’s a look at some of these materials, and what needs to be done to dry them.
Read More




.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)