How Graham Packaging Counters PCR Supply/Demand Squeeze
Customers want more PCR—including food grade—than recyclers can supply. Solutions involve efforts to educate customers, employees, and the community at large. New technologies also offer hope.
With demand for recycled plastics content—especially post-consumer—growing faster than the supply, plastics processors are feeling the squeeze. That’s true for even the largest users of post-consumer recycle (PCR), even one that has its own bale-to-pellet recycling capability. The company in question is Graham Packaging Co. (grahampackaging.com), a producer of more than 16 billion rigid containers per year from HDPE, PP and PET. Based in Lancaster, Pa., GPC has over 60 facilities employing almost 5000 people in 16 nations in North and South America, Asia and Europe.
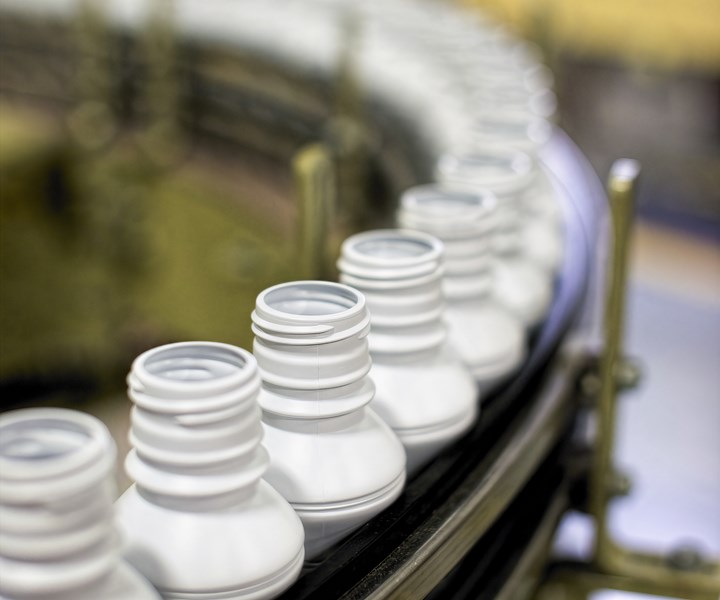

Graham, a leading global bottle maker aims to make its own products easier to recycle as a contribution to increased PCR supply. Scarcity of food-grade rHDPE is an ongoing concern.
According to Graham’s 2018 Sustainability Report (short.ptonline.com/SustainRpt), the company used 65 million lb of PCR HDPE (rHDPE) that year, of which 42 million lb, roughly the equivalent of 300 million plastic containers (mostly milk jugs), was processed from raw bales by the Graham Recycling Center in York, Pa. The rest came from a network of 10 other recyclers coast to coast. Graham uses natural and a small amount of colored rHDPE. In addition, the company consumed 18.1 million lb of its own HDPE regrind. Overall, that amounted to 12.4% of the HDPE processed by Graham Packaging in 2018.
Graham also used 11 million lb of clear (not colored) rPET from food/beverage packaging in 2018, all of which came from other recyclers. That equaled 2% of the 550 million lb of PET processed by Graham that year.
“We’re caught between wanting very much to increase use of recycled plastics in our products and lack of availability and higher costs.”
Feeling the Squeeze
“We’re seeing an uptick in interest in using recycled material from customers and end consumers,” says Tracee Auld, chief sustainability officer at Graham Packaging. “The requests are coming from across the board—food, beverage, household and automotive products. We see requests from customers to increase the level of PCR, and from others who never asked for it before. And the interest is getting more specific, such as for food-grade rHDPE, which is in very, very limited in supply in the U.S.”
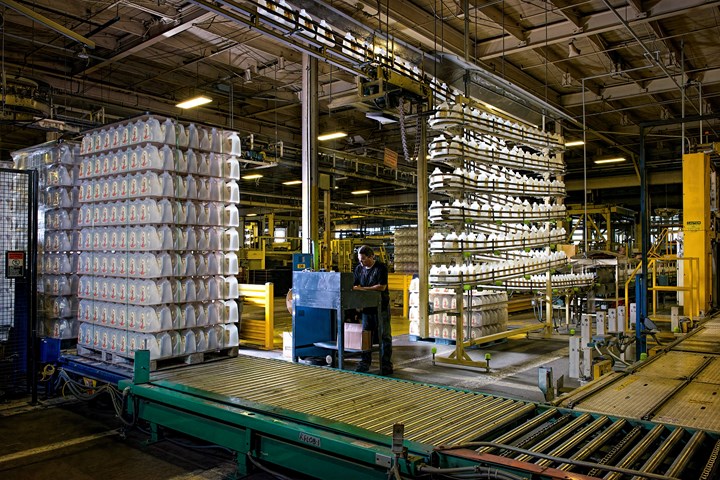

Graham Packaging uses around 80 million lb/yr of rHDPE and rPET, plus about 20 million lb of reground process scrap.
On the other hand, she notes, “We’re not seeing an increase in recycling activity to increase the amount of PCR feedstock available. So we’re caught between wanting very much to increase use of recycled plastics in our products and lack of availability and higher costs.”
Graham has supplied customers with bottles containing from 10% to 100% recycled material, though the typical range is 20% to 40%, with PET containers at the low end and HDPE containers at the higher range. Both HDPE and PET containers can be supplied as monolayer blends with recycle, or in multilayer structures with regrind/recycle in a specific layer. For PET stretch-blow molded containers, Graham has a technology it calls Surshot for injection molding three-layer PET preforms with up to 40% recycle in the center layer.
“Food-grade rHDPE is in very, very limited in supply in the U.S.”
Auld dispels any notion that the Chinese government’s suspension of imports of U.S. plastic waste has had a beneficial effect on the supply of PCR for domestic users like Graham. “What was going over there was mainly lower-grade, contaminated reclaim that is not used here and is not very suitable for mechanical recycling.”
So, what can processors like Graham do to ease the squeeze? The answer, according to Auld, is in broad-based education. That begins by educating customers in design-for-recycling principles. “We are addressing the squeeze indirectly,” says Auld, by making sure our products are easy to recycle.” Just a year ago, Graham Packaging joined hundreds of the world’s leading packaging brands in signing on to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation New Plastics Economy Global Commitment, which states that, by 2025, 100% of members’ plastic packaging can be reused, recycled or composted (newplasticseconomy.org)
Auld says customer education includes introducing them to design-for-recyclability principles espoused by the Association of Plastics Recyclers (APR, plasticsrecycling.org), which include considering not just the resin, but the choices of label, glue and closure for maximum recyclability. “We also talk to them about using both PCR and PIR (post-industrial regrind), regardless of whether legislative mandates (such as those in California for 25% PCR in nonfood packaging) don’t give credit for PIR.”
Auld adds that Graham talks with customers about what to expect from PCR. For one thing, and perhaps contrary to some expectations, PCR is generally more expensive, she notes, driven by high demand for limited supplies. Another factor is that “PCR has from a small-to-moderate negative effect on productivity in processing,” owing to the greater inherent variability in the raw material. There can also be issues with contamination and color variation. Auld points out that some makers of laundry detergents go so far as to make a marketing point of the more muted and variable colors of containers with PCR as a recognizable signal of sustainability to savvy consumers.
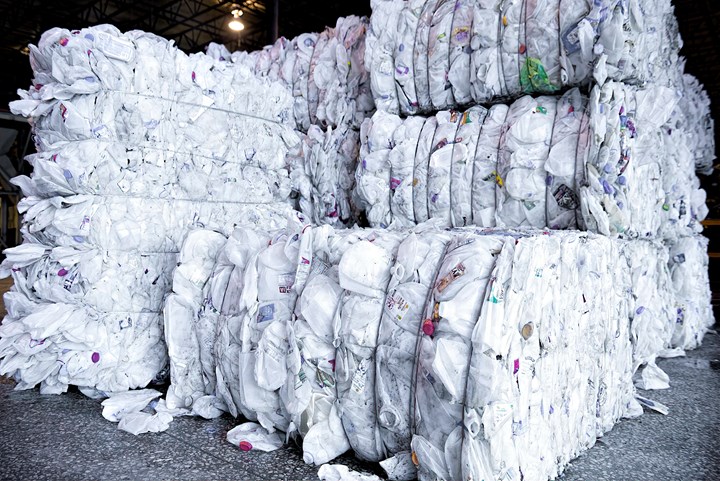

The Graham Recycling Center processes 50 million lb/yr of HDPE bales, consisting mainly of milk jugs.
Balaji Jayaseelan, Graham’s newly appointed director of Sustainability and Regulatory Affairs, notes that Graham has policies and procedures to ensure as much consistency as possible in its recycled materials. “We deal with the top 10 to 15 suppliers of recycled pellets and have had a detailed certification process for 30 years.” The Graham Recycling Center has specifications on rHDPE bales—pigmented, unpigmented, or mixed—for example, calling out maximum levels of contaminants of various sorts. For shipments of purchased rHDPE pellets, Jayaseelan says, “We check the certificate of compliance to ensure that the product conforms to our specs for density, MI, color, moisture level and fines. For rPET, Graham looks at IV, color and levels of moisture and fines. “We do audit suppliers to ensure their quality control and test procedures are accurate and up to all our requirements. We also take readings on our finished product (bottles or preforms) to ensure we are in spec for color and other properties.”
“We are addressing the supply/demand squeeze indirectly by making sure our products are easy to recycle.”
Educating the Community
Auld says education is a priority not just for customers. It’s vital to educate consumers at large to support—and demand—greater recycling activity. “We start with our people, educating our employees and their families about the value of recycling. We also joined and help fund the Recycling Partnership, a nonprofit organization dedicated to increasing and improving recycling in states, cities and communities across the U.S. (recyclingpartnership.org). Besides Graham, the 50+ funding partners range from major brand owners (Coca-Cola, Pepsico, Amazon, Procter & Gamble and others) to resin producers (including Dow, ExxonMobil and Indorama), other large processors (Amcor, Berry Global, Dart, Sonoco), industry associations and the U.S. EPA. “We’re breaking barriers in our communities to increased recycling,” Auld explains.
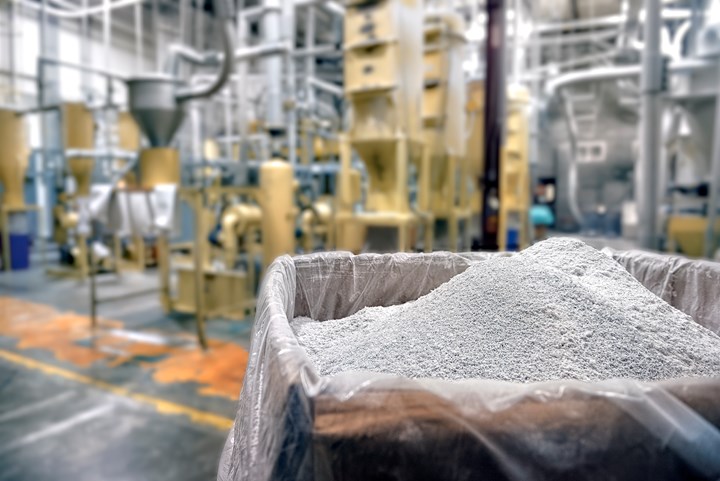

Mechanical recycling, used at the Graham Recycling Center, can handle high-quality post-consumer scrap. For the future, Graham looks to innovations like chemical recycling to salvage more low-quality plastic waste.
Looking Ahead
The Graham Recycling Center—one of the largest of its kind in the Northeast, employing 50 people—increased its output of rHDPE pellets by 19% to 50 million lb last year, consuming around 378 million plastic containers from curbside recycling programs. “Our own recycling capacity is under pressure and currently meets only a little more than half our PCR needs,” Auld says. The Recycling Center began with one line in 1990 and has since grown to three lines. Besides further expansion, among the possibilities under consideration is adding rPET to the Recycling Center’s activities.
Auld believes that “the demand for recycle will force innovation. Packagers will learn to design responsibly so that less low-quality PCR results. And the recycling industry must evolve to deal with a wider range of materials.”
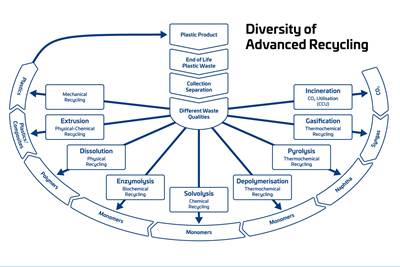
In particular, Auld and Jayaseelan have their eyes on the emerging field of chemical recycling via depolymerization or solvent purification. “We’re very excited about such innovations and what they might mean for reclaiming low-grade PCR. But it’s significance is for the long run.”
Related Content
Joint Venture Will Build Largest Mechanical Recycling Plant in India
Lyondell Basell and Shakti Plastic Agreed to Build and Operate Plant to Process PCR
Read MoreIgus Unveils World’s “First” Urban Bike Made from Recycled Plastic
The engineering concept and key components for bikes made of recycled plastic are available to all bike manufacturers.
Read MoreA Recycling Plant, Renewed
Reinvention is essential at Capital Polymers, a toll recycler that has completely transformed its operation in a short period of time.
Read MoreRecycling: What's Ahead in Advanced Sorting Technology
As the industry tries to ramp up recycling, there are several innovative sorting solutions in the offing—ranging from enhanced optical sorting technologies and chemical tracers to advanced solutions based digital watermarks and artificial intelligence.
Read MoreRead Next
Processor Turns to AI to Help Keep Machines Humming
At captive processor McConkey, a new generation of artificial intelligence models, highlighted by ChatGPT, is helping it wade through the shortage of skilled labor and keep its production lines churning out good parts.
Read MorePeople 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
Read MoreAdvanced Recycling: Beyond Pyrolysis
Consumer-product brand owners increasingly see advanced chemical recycling as a necessary complement to mechanical recycling if they are to meet ambitious goals for a circular economy in the next decade. Dozens of technology providers are developing new technologies to overcome the limitations of existing pyrolysis methods and to commercialize various alternative approaches to chemical recycling of plastics.
Read More


















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)