Nonlinear Modelling: A Proven Mathematical Tool for Efficient Product Development
This approach been shown to be beneficial to crosslinked foam producers and applicable to other types of plastics processors.
A mathematical tool that proved to be an effective approach to save time, money and effort in product development for foam extruders, can also be used by various types of plastics processors.This was recently brought to our attention by Abhay Bulsari, owner and president of a Finland-based 22-year-old process and materials development consultancy called Nonlinear Solutions Oy. Here, Bulsari gives us the example applying linear modelling in his work with Finnish PE foam extruder NMC Termonova.
Bulsari’s goal was to help speed up the company’s product development, which included not only improving the quality of its foamed products, but also how to produce better recipes and new products with more demanding combinations of material properties. Explains Bulsari, “We have established how nonlinear models are a powerful tool for materials development as they can contain valuable knowledge in a concise and precise form. A small number of experiments suffices for the development of nonlinear models, if planned suitably. Material properties can be related with the composition variables, process variables and dimension variables effectively using nonlinear modeling.”
NMC Termonova produces crosslinked, foamed LPDE products using the Furukawa process, according to Markku Talja senior production chemist. The raw LDPE polymer is mixed with a crosslinking agent and a blowing agent and fed to an extruder which produces a thin and wide sheet—or, a matrix. It is then fed to an oven, where it is crosslinked and foamed. The foam is then cooled with water and wound into rolls.
Keep the ‘Wider Picture’ in Mind & Apply Nonlinear Modeling
Among the key applications of foamed plastics is thermal insulation. Like material properties of various kinds of materials, thermal conductivity also depends on the composition variables, process variables and dimension variables, explains Bulsari. “Since one material property often comes at the cost of another, and could affect the production economics, it is desirable to keep the wider picture in mind, which includes several consequences of operating the process. Once we know quantitatively how these variables affect the various consequences, we can determine good or optimal values of those compositions, process and dimension variables to achieve a desired combination of product properties, production rate and production cost.”
The relation between these variables is usually not expected to be very simple or linear. Mathematical models can be used instead of experimentation if they are sufficiently reliable. They can be used to improve quality, make changes in processing, as well as determine ways to produce new products with desired combinations of product properties, or with lower costs. Says Bulsari, “Mathematical modeling can be carried out in different ways and the different approaches are suitable in different situations. However, conventional techniques of empirical modeling are linear. Nothing in nature is very linear, and materials science is full of nonlinearities.”
In contrast, it has been established that feed-forward neural networks—a kind of mathematical modeling approach and more recently a part of artificial intelligence—now increasingly used by R&D people, do not require the knowledge of the type of the nonlinearities in advance. “They are attractive for nonlinear modelling because of their universal approximation capabilities which make them very suitable for most function approximation tasks we come across in materials science and process engineering. The user does not need to know the type and severity of nonlinearities while developing the model,” explains Bulsari. There are many different types of neural networks, and the multilayer perceptron, a kind of feed-forward neural network, is the most common one. They have been in use for over 20 years and have benefited process industries including plastics, composites, rubbers, and chemicals.
Product properties including thermal conductivity depend on the amount of polymer, blowing agent, crosslinking agent, etc. Prior to conducting well-planned experiments and developing nonlinear models, NMC Termonova would conduct trial-and-error experiments when they saw a need to improve something. This is a common approach for many plastic processors, but is fairly inefficient. It requires a lot of experimentation, and the final result may not be very good, according to Bulsari.
Working with this foam extruder, Bulsari developed neural network models for several material properties like thermal conductivity, density, slab thickness, tensile strength, and also for production economic variables, from 38 experiments carried out for this project. It was shown that with appropriate mathematical tools, such models can be used to determine ways to produce foam with desired values of thermal conductivity in combination with limits on strength, density, etc. “If the combination is impossible with the raw materials in use, we would know it very quickly without spending a lot of time and effort in experimentation. We are able to use the same models also to determine ways to reduce production costs,” says Bulsari.
In conclusion, he confirms that he worked with several of NMC Termonova’s existing recipes and using the nonlinear models calculated new recipes for the same products, all of each are lower in cost by at least a few percent.
Related Content
Fundamentals of Polyethylene – Part 5: Metallocenes
How the development of new catalysts—notably metallocenes—paved the way for the development of material grades never before possible.
Read MoreCommodity Resin Prices Flat to Lower
Major price correction looms for PP, and lower prices are projected for PE, PS, PVC and PET.
Read MorePolyethylene Fundamentals – Part 4: Failed HDPE Case Study
Injection molders of small fuel tanks learned the hard way that a very small difference in density — 0.6% — could make a large difference in PE stress-crack resistance.
Read MoreIn Sustainable Packaging, the Word is ‘Monomaterial’
In both flexible and rigid packaging, the trend is to replace multimaterial laminates, coextrusions and “composites” with single-material structures, usually based on PE or PP. Nonpackaging applications are following suit.
Read MoreRead Next
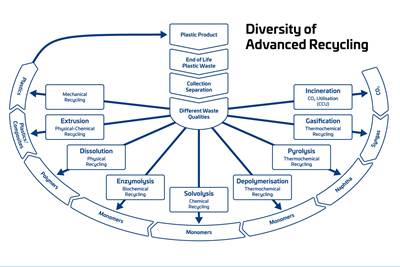
Advanced Recycling: Beyond Pyrolysis
Consumer-product brand owners increasingly see advanced chemical recycling as a necessary complement to mechanical recycling if they are to meet ambitious goals for a circular economy in the next decade. Dozens of technology providers are developing new technologies to overcome the limitations of existing pyrolysis methods and to commercialize various alternative approaches to chemical recycling of plastics.
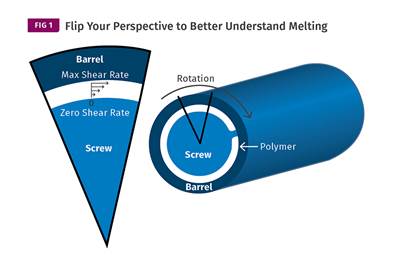
Read MoreUnderstanding Melting in Single-Screw Extruders
You can better visualize the melting process by “flipping” the observation point so that the barrel appears to be turning clockwise around a stationary screw.
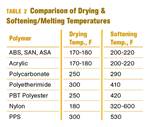
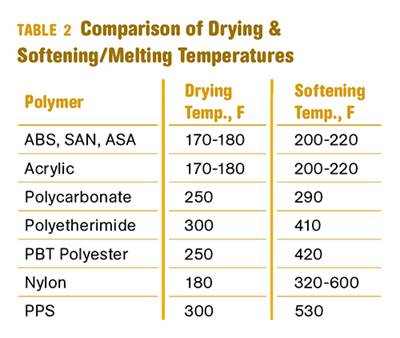
Read MoreWhy (and What) You Need to Dry
Other than polyolefins, almost every other polymer exhibits some level of polarity and therefore can absorb a certain amount of moisture from the atmosphere. Here’s a look at some of these materials, and what needs to be done to dry them.
Read More