Smart Electronics for Luminous, Smart, Sustainable Clothing
Covestro will “shine” at K 2016 showcasing an item of luminous clothing with a TPU formable film/copper laminate as key.

Covestro will “shine” at K 2016 showcasing an item of luminous clothing with a TPU formable film/copper laminate as key.
Our September pre-K 2016 issue includes a feature on materials and additives and you will notice that there is no shortage of new developments in those arenas. Expect to see some pretty exciting new applications showcased by most key suppliers.
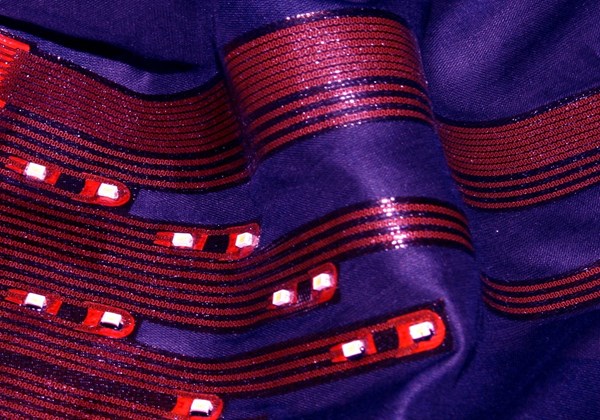
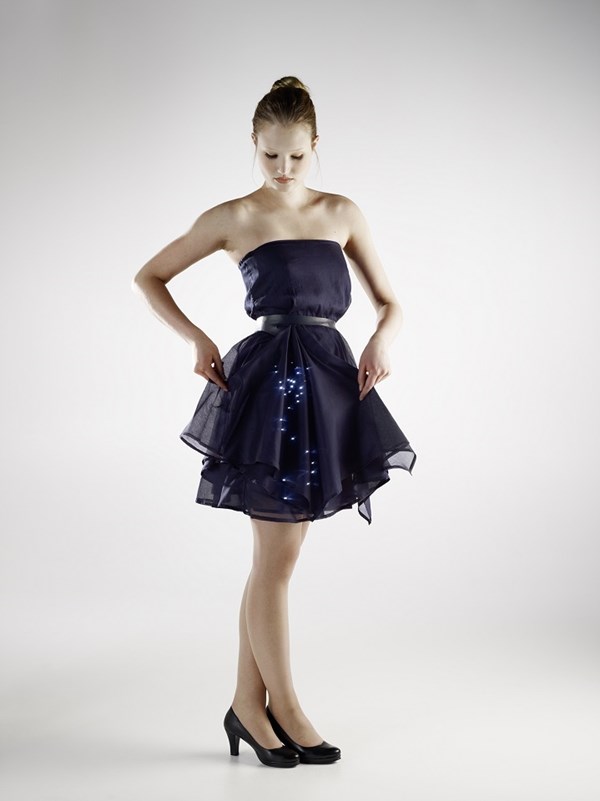
One example, is Covestro, Pittsburgh, Penn., which will showcase an item of luminous clothing that utilizes light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to make it stand out, but also can also perform key functions such as protecting pedestrians and cyclists against accidents. What makes it unusual is that the LEDs are not positioned on a panel or strip, but on a piece of soft fabric.
Central to this development is an electronic system that is responsive to movements without losing its functionality. This system comprises a flexible and formable film made from a Covestro TPU. It serves as the substrate for the printed copper circuits which are arranges in a meandering pattern and can thus also be bent and stretched.
This “intelligent” technology involves the manufacture of smart circuits using the following efficient, multi-stage process:
• First, copper films are laminated onto the TPU films.
• The printed circuits are produced in a subsequent structuring operation, which reportedly features highly-effective adhesion.
• The coated films are then shaped as required using conventional thermoforming.
According to Covestro film expert Wolfgang Stenbeck, the TPU films are resistant to standard etching and imaging processes. “Formable electronic systems can be directly laminated onto textiles, as is the case of the luminous dress,” he said.
This production technology is part of various projects funded by the EU Commission, among them STELLA and TERASEL. The objective is to product 2.4-dimensional electronic circuits cost-effectively using conventional forming processes. The freely-formed components can be integrated seamlessly into energy-efficient electronic components. They can be processed using standard PCB industry equipment and are also suitable for applications with higher currents or voltages. Compared to conventional electronic components, the smart circuits offer greater design freedom and reliability while enabling more sustainable products for a variety of industries due to the reduced use of materials. Here are some exciting applications this technology offers:
• There’s a wide range of options for smart textiles, alone. In addition to fashion items, freely-formable electronic systems are already in use in underwear, where they monitor heart rate and breathing. They assist patients with therapy and help athletes monitor their training.
• TERASEL technology also enables production of modular automotive interior components in which all functions are already integrated. It boasts reduced complexity in assembly, lower costs and shorter time to market. It is also said to clear the way for new lighting concepts in automotive interiors and buildings, where designers and architects can position LEDs exactly where they are most needed.
• In consumer electronics, smart circuits are supporting the trend toward increased miniaturization of components, as they can be incorporated directly into the outer shell of products.
• Stretchable circuit board (SCB) technology for manufacturing electronic circuits was developed earlier as part of the STELLA project. This was led by the Fraunhofer Institute for reliability and Microintegration (IZM) and the Technical University of Berlin. Coated TPU films can be stretched repeatedly up to 60%, and on a one-time basis by as much as 300%.

Related Content
Real-Time Production Monitoring as Automation
As an injection molder, Windmill Plastics sought an economical production monitoring system that could help it keep tabs on its shop floor. It’s now selling the “very focused” digital supervisor it created, automating many formerly manual tasks.
Read MoreAutomation Evolution: From Robots to Work Cells, Solo Devices to Integrated Systems
Injection molding automation has progressed from devices to systems, from simplicity to more complex capabilities. The author traces this development through various levels of automation – all still available choices today – and analyzes the costs and capabilities for each level.
Read MoreCobot Creates 'Cell Manufacturing Dream' for Thermoformer
Kal Plastics deploys Universal Robot trimming cobot for a fraction of the cost and lead time of a CNC machine, cuts trimming time nearly in half and reduces late shipments to under 1% — all while improving employee safety and growth opportunities.
Read MoreFive Ways to Increase Productivity for Injection Molders
Faster setups, automation tools and proper training and support can go a long way.
Read MoreRead Next
Lead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
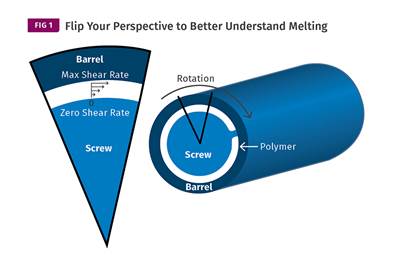
Read MoreUnderstanding Melting in Single-Screw Extruders
You can better visualize the melting process by “flipping” the observation point so that the barrel appears to be turning clockwise around a stationary screw.
Read MoreTroubleshooting Screw and Barrel Wear in Extrusion
Extruder screws and barrels will wear over time. If you are seeing a reduction in specific rate and higher discharge temperatures, wear is the likely culprit.
Read More