U.S. Plastics Sector Stars in Lackluster Global Economy
The U.S. plastics industry in 2014 succeeded despite a near-worldwide malaise, but how long can we thrive while our global partners falter?
The sustainability of that performance disparity was one topic tackled in a recent SPI webinar, which highlighted results from the association’s newest Global Trend Report.
In addition to a breakdown of the report’s finding by Michael Taylor, SPI’s International Affairs Director, the webinar included insights on the broader manufacturing environment by Cliff Waldman, director of economic studies at the MAPI Foundation, and a reshoring recap from Harry Moser of The Reshoring Initiative.
Where’s the Mojo?
The global economy is recouping from the economic shock of the Great Recession, but doing so on an uneven basis and without the vigor of previous recoveries.
“We have a world that lacks mojo,” Waldman explained. “Worldwide there is a dearth of the type of risk taking that is often the difference between sluggish growth and normal growth.”
Waldman acknowledged that “the U.S. is the only major economy that truly is looking better,” before asking, “the question is: will global economy bring it down?”
Plastics Power On
SPI noted that its data showed overall demand for plastics remains strong, with the U.S. holding significant market share over imports. “The U.S. plastics industry is healthy and getting healthier,” is how SPI President and CEO Bill Carteaux summed up the state of the sector ahead of its largest show.
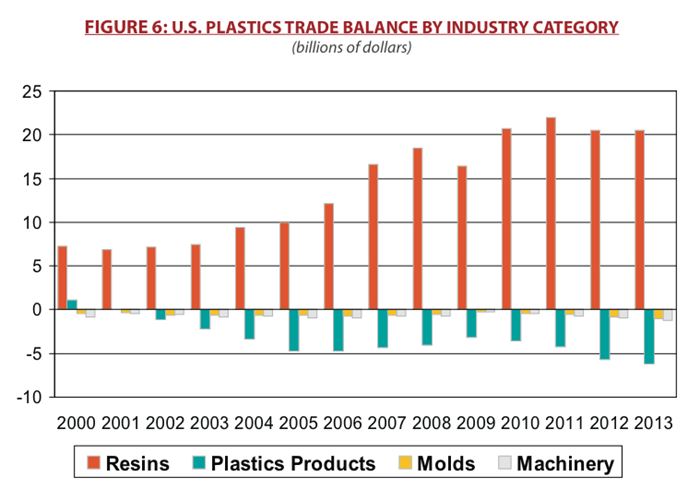
Consumption increased 6.5%, while exports of raw materials continued to show gains and the resin trade surplus grew. Overall exports rose 2.7%, minus machinery, but SPI expects a stronger equipment performance in 2015, with a bump from its triennial event, NPE2015.
Taylor noted that of the sectors with the largest net employment gains in 2014, plastics was No. 3, behind only fabricated metal and transportation equipment, creating more than 4000 net jobs.
Plastics also ranked high in production growth, trailing only furniture from October 2013 to October 2014. Plastics as a U.S. manufacturing sector has long enjoyed overall growth, according to Taylor, with plastics manufacturing employment up since 1980, while the value of manufactured shipments has grown 2.3% per year since that time.
Balancing Trade
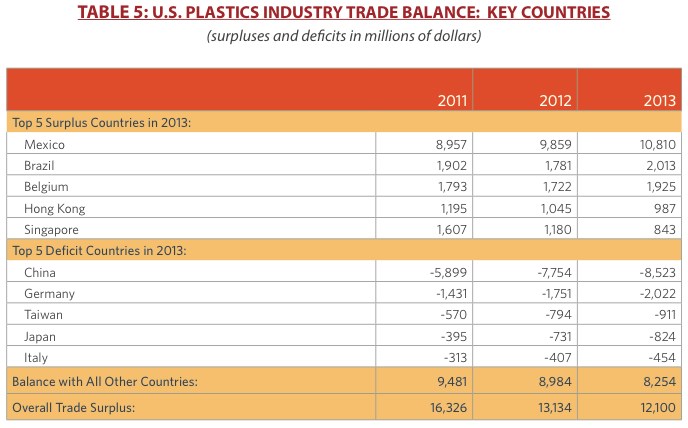
Industry exports rose 2.7%, while imports rose 5.8%. Mexico and Canada remain the largest export markets for the U.S. plastics industry, followed by China, Belgium and Brazil. Overall, the industry ended up with a positive trade balance, despite a trade deficit of $1.4 billion in machinery. The largest deficit was still with China, although it was smaller.
In terms of market share, domestically, resin held steady at 79.6%, while products (84.4%) and machinery (36.6%) saw their domestic segment increase. The U.S. market share for molds, however, shrunk to 54.7%.
Top Emerging Markets
The top growth markets for U.S. plastics exports in terms of percentage gains were Ukraine, Oman, Indonesia, Nigeria and Algeria. Going back to 2000, the top growth markets show some overlap with that group, as well as new players with Ukraine, Algeria, Vietnam, Ghana, and Nigeria.
Asked about the growing trade deficit in finished goods, Taylor stressed the overall trade surplus for the sector. “Our largest trade deficit, with China, actually decreased,” Taylor said, “and we hope continue to go in right direction. Whether we will every get out of a deficit with a trading partner like China, that’s not really possible.”
Moser sounded a hopeful tone on China, at least in terms of reshoring. Noting that China’s unit labor costs have gone up 400% since 2000, Moser, who often caps presentations with an image of the little Dutch boy trying to plug the leaky dike, revealed data showing what may already be a fully functioning seawall.
As opposed to 2003, when U.S. manufacturing was losing 148,000 jobs per year to offshoring, the balance of jobs reshored and offshored in 2013, was net zero. Next year, the tide is anticipated to shift, with a net gain in manufacturing jobs. “About 60% of the reshoring has been from China,” Moser said, noting that the country is “showing a lot of vulnerability.”
Getting the Mojo Back
So what would it take for a tepid U.S. recovery to become a full-fledged global growth cycle: reinvigorated entrepreneurship. “I think we need to encourage entrepreneurship,” Waldman said. “There currently are two kinds of risk-taking that U.S. and the world are short of: one is capital investment, and two, we’re very weak on business start ups, and that’s really why we’ve had such a slow labor market turn. We need to do the things that encourage business start ups, create more of the entrepreneurial environment of ‘80s and ‘90s.”

Related Content
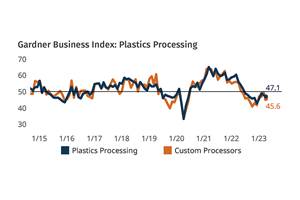
Plastics Processing Growth Slows Slightly
May reading for plastics processors is, for the most part, a continuation of what we saw in April.
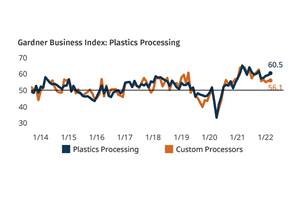
Read MorePlastics Processing Continued Contraction in April
Despite some index components accelerating and others leveling off, April spelled contraction for overall plastics processing activity.
Read MoreNPE2024 and the Economy: What PLASTICS' Pineda Has to Say
PLASTICS Chief Economist Perc Pineda shares his thoughts on the economic conditions that will shape the industry as we head into NPE2024.
Read MoreRead Next
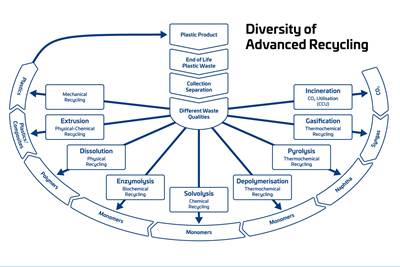
Advanced Recycling: Beyond Pyrolysis
Consumer-product brand owners increasingly see advanced chemical recycling as a necessary complement to mechanical recycling if they are to meet ambitious goals for a circular economy in the next decade. Dozens of technology providers are developing new technologies to overcome the limitations of existing pyrolysis methods and to commercialize various alternative approaches to chemical recycling of plastics.
Read MoreProcessor Turns to AI to Help Keep Machines Humming
At captive processor McConkey, a new generation of artificial intelligence models, highlighted by ChatGPT, is helping it wade through the shortage of skilled labor and keep its production lines churning out good parts.
Read More