VCM in the News Again, Not in a Good Way
Those three letters, V-C-M, stood out from the headlines of the toxic train wreck in Ohio this past week — bringing up echoes of a time that few may remember today, when the vinyl industry was in an uproar over reports of VCM hazards in the workplace and possibly in PVC food packaging.

Prominent mention of VCM as a threat to residents of East Palestine, Ohio, after the freight-train derailment there brought back memories of researching our December 1974 cover story on the crisis in the vinyl industry caused by recognition of VCM toxicity in the workplace.
The horrific consequences of the Feb. 3 derailment of a freight train carrying hazardous chemicals in East Palestine, Ohio have ignited a firestorm of public debate on railway transport safety, environmental monitoring and cleanup, and protection of the people living and working in the area of chemical exposure, as well as downstream communities potentially exposed to the toxic runoff.
By now, the noxious smoke has dispersed and most or all of the physical wreckage has been hauled away from the site of the crash, close by the Ohio-Pennsylvania line between Youngstown and Pittsburgh. But nagging concerns no doubt remain for many families in the area about potential long-term effects from whatever caused all the headaches, rashes, burning eyes and throats, dead chickens and fish and moribund foxes and other wildlife.
According to various reports, among the 38 railcars that derailed, 10 were carrying a witches’ brew of nasty-sounding chemicals you wouldn’t want loose in your air or water: isobutylene, butyl acrylate, ethylhexyl acrylate, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, benzene residue and — the one that caught my particular attention — vinyl chloride monomer, or VCM.
Apparently, VCM was also the one bit of freight cargo that attracted most concern from first responders, whether because those five railcars — each of which could have been carrying upwards of 31,000 gallons—were in the greatest danger of exploding from the fires among the wreckage, or because Ohio health and safety officials had prior experience with VCM, dating back to another spate of dramatic headlines a half-century ago.
I remember those headlines well, because I wrote some of them. The spark that set it all off was the voluntary announcement in January 1973 by B.F. Goodrich, then the biggest U.S. vinyl resins manufacturer, headquartered in Ohio, of the deaths of three long-time workers in its Louisville, Ky., PVC plant from a very rare cancer, angiosarcoma of the liver. Subsequent intensive search in the U.S. and Europe turned up more than two dozen cases of this disease among workers in vinyl monomer and polymer production and PVC processing. I learned that the industry had been so casual about VCM exposure up to that time that workers allegedly “cooled their Cokes” in buckets of VCM, because it evaporated quickly, drawing off heat.
Soon after Goodrich’s announcement (yes, they blew the whistle on themselves), the one-year-old Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) issued an Emergency Temporary Standard limiting employee exposure to VCM to one-tenth the prior limit. And the Federal Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco & Firearms revoked its 1969 approval for use of PVC in liquor bottles, and all PVC food packaging fell under suspicion. That suspicion was not totally unwarranted, as it was discovered that the PVC of that time contained substantial amounts of residual monomer — something that was promptly and comprehensively remedied by the industry, much of which was then located in Ohio.
In my second year on the job, I became the one on our very small editorial staff at that time to follow this story. I attended a hastily called and heavily attended emergency SPE conference addressing the VCM crisis, and then I wrote an eight-page cover story for our December 1974 issue, “Living with VCM: How PVC Processors Can Cope.” I stuck with the story for about a decade, as the industry struggled unsuccessfully to get the FDA to declare that PVC was safe for food and beverage packaging. For what I deemed to be mostly political reasons, FDA indicated it would not object to PVC food and beverage packaging, but refused to affirm its safety, despite endless studies showing that VCM migration from PVC into foods and beverages was now undetectable in testing sensitive to the parts-per-billion range.
So, yes, my attention was riveted when I heard TV announcers last week struggling to pronounce “vinyl chloride monomer” as if it were from an alien language, and when they called in their “medical experts” to pronounce breathlessly that this colorless, odorless (untrue) VCM gas was known to cause cancers of the liver, lung, blood, brain and breast. The better reports stated that VCM was carcinogenic in long-term exposure to high levels, and most reports focused appropriately on the byproducts of the “controlled” burnoff of VCM deliberately vented from overheated tank cars — byproducts like hydrochloric acid (HCl) and phosgene, a poison gas used as a deadly weapon in World War I. But my ears were ringing from some of the most sensational pronouncements from TV “experts,” for example: “Of course, the greatest concern was vinyl chloride because this is one of the most toxic, poisonous chemicals on the planet!” I’m quite sure a teaspoon of pure VCM would hardly compare in lethality with an equal amount of fentanyl, cyanide or radioactive polonium (allegedly used to assassinate “inconvenient” Russian expatriates).
As if the 5000 residents of East Palestine were not burdened enough by this catastrophe and the questionable guidance they were getting to return home so soon and that the air and water around them were safe (despite suspicious “sweet smells in the air and dead fish in the river)—they also had to bear such apocalyptic alarmism from TV news channels. I was saddened to hear such wide-eyed blather from medical sources I had previously regarded as rational and knowledgeable sources on topics such as Covid. So why did they fall so far short when dealing with a subject that I happened to know something about?
I think the answer lies in the procedures of TV news, which seem to be to ask medical doctors to pronounce on subjects unfamiliar to them — like an occupational disease seen mainly in the vinyl industry 50 years ago — based on the briefest research preparation, probably a sheet of bullet points prepared by a studio assistant. Not once on TV news, in New York newspapers or an (admittedly brief) online search did I encounter any reference to sources like the American Chemistry Council, the plastics trade society (PLASTICS) or the Vinyl Institute when it came to VCM toxicity. Why do you suppose that is?
Related Content
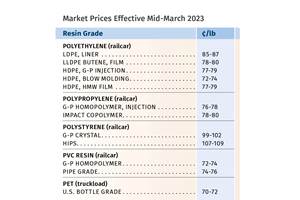
Prices of Volume Resins Generally Flat or Lower
Exceptions in early March were PP and PS, which moved up solely due to feedstock constraints, along with slight upward movement in PVC and PET.
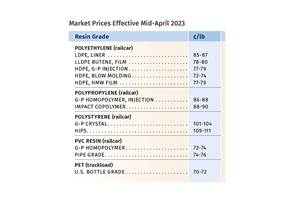
Read MoreFirst Quarter Looks Mostly Flat for Resin Prices
Temporary upward blips don't indicate any sustained movement in the near term.
Read MorePP Prices May Plunge, Others Are Mostly Flat
PP prices appear on the verge a major downward trajectory, with some potential of a modest downward path for others.
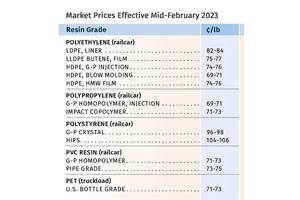
Read MoreCommodity Resin Prices Flat to Lower
Major price correction looms for PP, and lower prices are projected for PE, PS, PVC and PET.
Read MoreRead Next
Lead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
Read MoreHow Polymer Melts in Single-Screw Extruders
Understanding how polymer melts in a single-screw extruder could help you optimize your screw design to eliminate defect-causing solid polymer fragments.
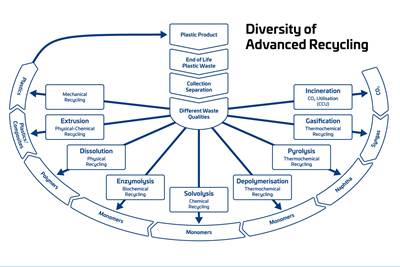
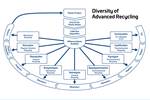
Read MoreAdvanced Recycling: Beyond Pyrolysis
Consumer-product brand owners increasingly see advanced chemical recycling as a necessary complement to mechanical recycling if they are to meet ambitious goals for a circular economy in the next decade. Dozens of technology providers are developing new technologies to overcome the limitations of existing pyrolysis methods and to commercialize various alternative approaches to chemical recycling of plastics.
Read More










.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)