Plastics Additives
Additives are materials that are added to the primary resin during either compounding or processing to improve the polymer’s processability, performance or appearance. Additives include colorants; heat stabilizers; process aids; fillers; compatibilizers; blowing agents; lubricants; slip agents.

ESSENTIAL READING
VIEW ALLUnderstanding the ‘Science’ of Color
And as with all sciences, there are fundamentals that must be considered to do color right. Here’s a helpful start.
Read MoreWhat’s With All the Static?
Static buildup on polymers can cause a variety of problems, some rather unpleasant. Yet there’s an inexpensive way to eliminate it, and we have data as proof.
Read MorePart 11: A Processor's Most Important Job
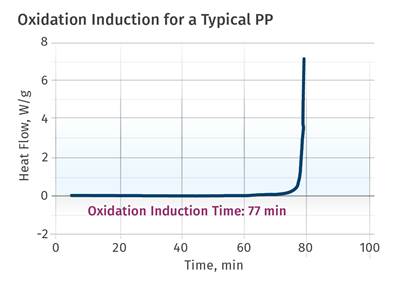
It’s the processor’s job to ensure molded parts contain enough stabilizer to perform to the expectations of the end use.
Read MoreHow to Prevent Stress Whitening in PP Copolymers
A look at causes, detection, and prevention.
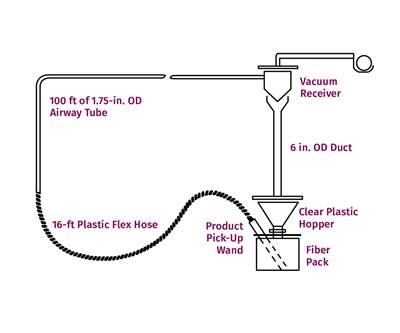
Read MoreExtruding with Fillers
You can use the reference point from processing unfilled polymer to determine whether you can run filled resin on your current system.
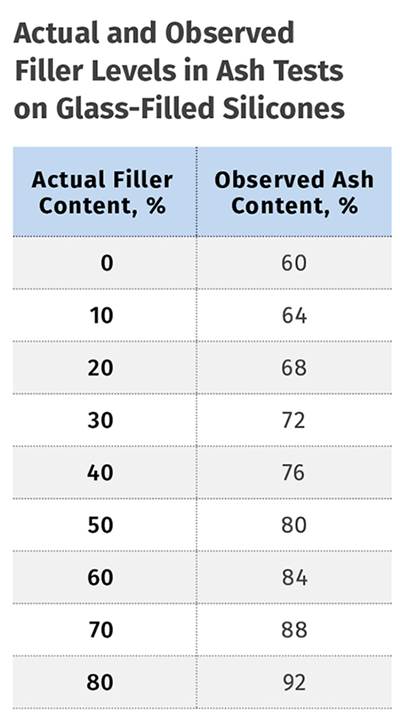
Read MoreMaterials: Analyzing Filler Content
The process is considered simple. But things aren’t always as they seem.
Read MoreLatest Additives News And Updates
OQ Introduces Clarified Random Copolymer Polypropylene Grade for Injection Molding
OQ’s Luban RP2251T uses Milliken clarifier.
Read MoreCAI Announces Flame-Retardant Masterbatch
ST-FR309 provides fire protection for polyester-based materials.
Read MoreBASF Additive Enhances Chemical Resistance of Greenhouse Films
BASF expands additive portfolio for agriculture applications.
Read MoreStruktol RP 17 and RP 53 Additives for Odor Control
Additives engineered to optimize processing, improve quality and facilitate increase in recycled content.
Read MoreAvient Introduces Oxygen Scavenging Additive
ColorMatrix Amosorb Oxyloop to enhance recyclability.
Read MoreKisuma Setogem RD for PP Nucleation and Acid Scavenging
Kisuma Chemicals has introduced a dual-purpose product for polypropylene producers.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
PT Tech Days Kicks Off Tuesday With Sustainable Materials
Presenters on September 9 will focus on alternatives that enable more sustainable plastic products.
Read MoreGraphene Turns 20: Two Decades of Innovation in Graphene-Enhanced Polymers
First isolated in 2004 and earnings its inventors the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010, graphene has only been on the scene for two decades but its growth and impact in plastics is undeniable.
Read MoreReplacing PFAS, a Transition in Processing Lubricants
Chemical manufacturers, polymer compounders and converters are making moves toward PFAS-free.
Read MoreCalcium Carbonate From Carbon Capture for Brighter Plastics and Greener Steel
CarbonFree is converting steel slag and blast furnace exhaust into an important plastic compounding additive.
Read MoreAdditives Boast Sustainability Without Sacrificing Performance
Sustainability continues to dominate new additives technology, but upping performance is also evident. Most of the new additives have been targeted to commodity resins and particularly polyolefins.
Read MoreStruktol Showcasing a Range of Specialty Additives
NPE2024: Focus is on additives for plastics including PVC and WPC industries.
Read MoreFAQ: Additives
What to consider when adding color?
There are several key items that are essential in developing a colorant package for any polymer. The first of these is the avoidance of any chemical incompatibility between the chemistry of the polymer and the chemistry of the colorant system. Chemical reactions proceed more rapidly at higher temperatures, and melt processing involves significantly elevated temperatures and large inputs of mechanical energy. Therefore, any chemical interactions that may occur between a polymer and a colorant system will happen very rapidly during the injection molding process.
The material supplier will incorporate a certain amount of the stabilization package in the material, making this the starting point for that material. It is now the processor’s job to handle the material during processing so that the molded part contains enough stabilizer to perform to the expectations of the end user. The molding process will always consume some amount of the antioxidant in the material. This is expected. But the amount of stabilizer that is consumed will depend upon the process conditions, most notably the melt temperature and the time the material spends in the molten state. Lower melt temperatures and shorter residence times will produce parts that retain a higher level of stabilization, and these parts will be more capable of handling the application environment. If melt temperatures become elevated or residence times become extended, the molded part will be less capable of managing the application demands.
Additives Supplier Categories
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing/Prototyping Materials)
- Antiblocking Agents & Concentrates
- Antioxidants & Concentrates
- Fillers - Mineral or Other Inorganic Type
- Compatibilizers
- Thixotropic Agents
- Biocides
- Color Concentrates
- Plasticizers
- Processing Aids (Organic & Inorganic)
- Release Agents (External & Internal/Additive)
- Odor Neutralizers
- Impact Modifiers
- Surface Treatment Chemicals, Dispersion Aids (for Fillers, Pigments, Reinforcements)
- Degradation Promoters
- Ceramic Fibers
- Metal Deactivators
- Continuous Fiber Rovings, Tows, Yarns
- Core Materials
- Carbon or Graphite Fiber
- Fillers -Organic Type
- Cooling-Water Treatment Chemicals
- Mineral Fiber
- Heat-Distortion Modifiers
- Fabric, Mat, Veil, Felt
- Stock Shapes - Film, Rod, Tube, Sheet
- Blowing Agents (Chemical, Physical, Concentrates)
- Resin Clean-up Solutions
- Viscocity Depressants
- Aramid Fiber
- Lubricants & Lubricant Concentrates
- Stripping Agents, Resin Removers
- Nylon, PET or PP Fiber
- Surfactants
- Color Dyes, Pigments
- Purging Compounds
- Air Release Agents
- Antistats & Concentrates
- Flame Retardants & Smoke Suppressants
- Fillers -Microspheres (Hollow or Solid)
- Nucleating/Clarifying Agents
- Conductive Additives
- Crosslinking Agents for Thermoplastics
- Slip Agents & Concentrates
- Antifogging Agents
- Heat Stabilizers for PVC
- UV Stabilizers & Concentrates
- Dessicant Additives
- Fragrance Additives
- Biodegradable, Photodegradable Resins & Compounds
- UHMW-PE Fiber
- Glass Fiber
- Natural Fibers
- Discontinuous Fibers (Chopped, Milled, Staple)